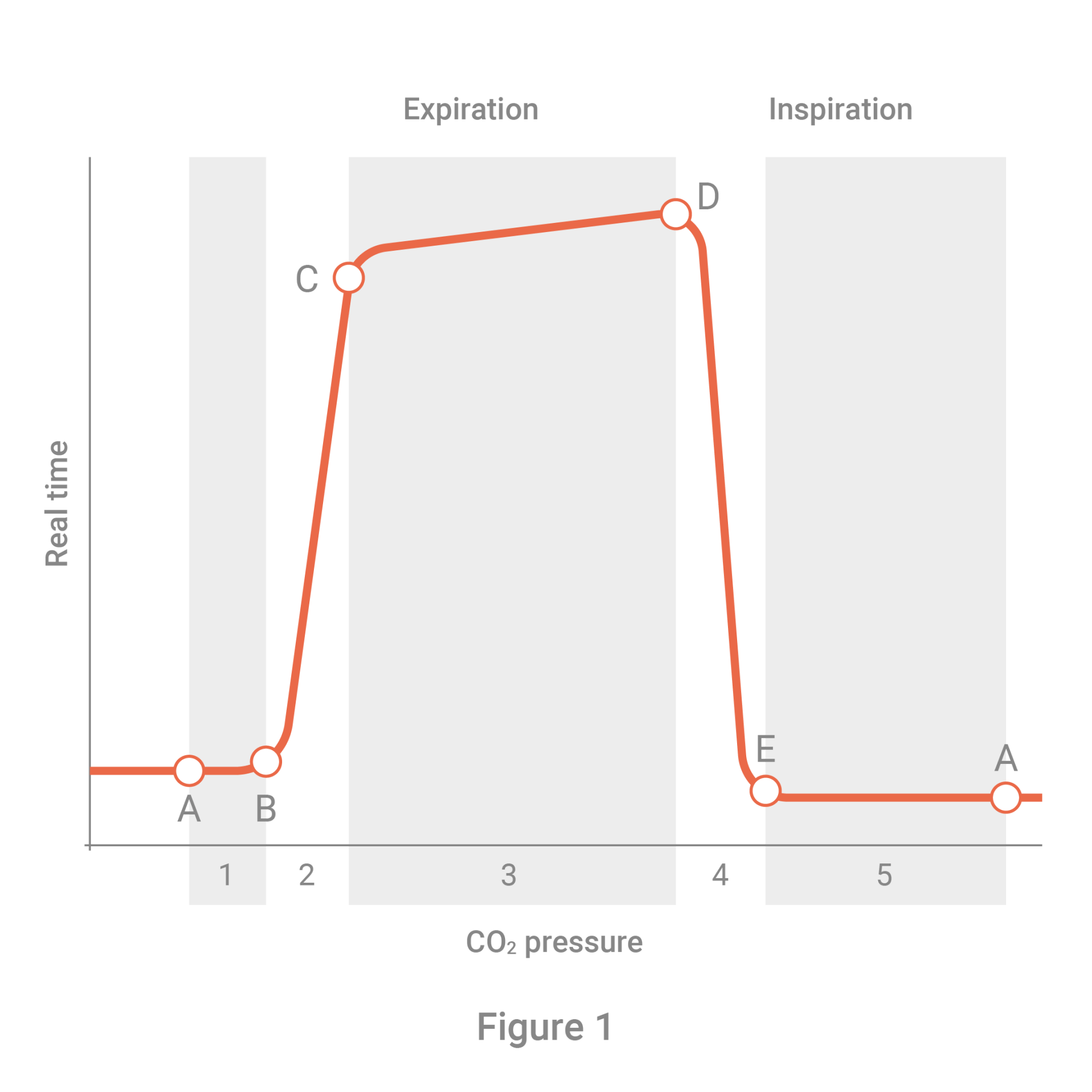
end tidal co2 range cpr
Since problems with lungs are not common and gas exchange between alveoli and the blood is swift and effective. Literature search was performed using Medline and EMBASE.

Pdf Applications Of Capnography In Airway Management Outside The Operating Room Semantic Scholar
End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detection requires air movement in and out of the lungs ventilation CO2 production from cellular metabolism and.
. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition. Throughout the resuscitation end-tidal CO 2 was consistently in the 28-36 mmHg range during VFCPR. More Than Just a Number.
10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. Chest compression provider tiring end-tidal CO2 value diminishes over time. Gradual fall in ETCO2 suggests compressionist fatigue during CPR - time to change compressionists.
High quality CPR consistent waveform and end-tidal CO2 20 kPa. Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg. During cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR adequate chest compressions generate a cardiac output of 17 to 27 allowing CO 2 circulation for exhalation.
Approximately 70 of CO 2 produced by the mitochondria undergoes a chemical reaction with water catalysed by carbonic anhydrase to form H 2 CO 3 dissolved in the plasma as its component ions HCO 3 - and H Another 23 of CO 2. Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. An accurate early predictor of the outcome of resuscitation is needed.
CO 2 is produced by the mitochondria as a major end product of tissue aerobic respiration. PetCO2 partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide. 423 20 mmHg versus 34 255 mmHg.
Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. In conditions of normal breathing 6 Lmin 12 breathsmin 500 ml for tidal volume etCO 2 is very close to alveolar CO2. Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation CPR ETCO2 concentration is a reliable index of effective heart compression during CPR which is associated with cardiac output 7 8.
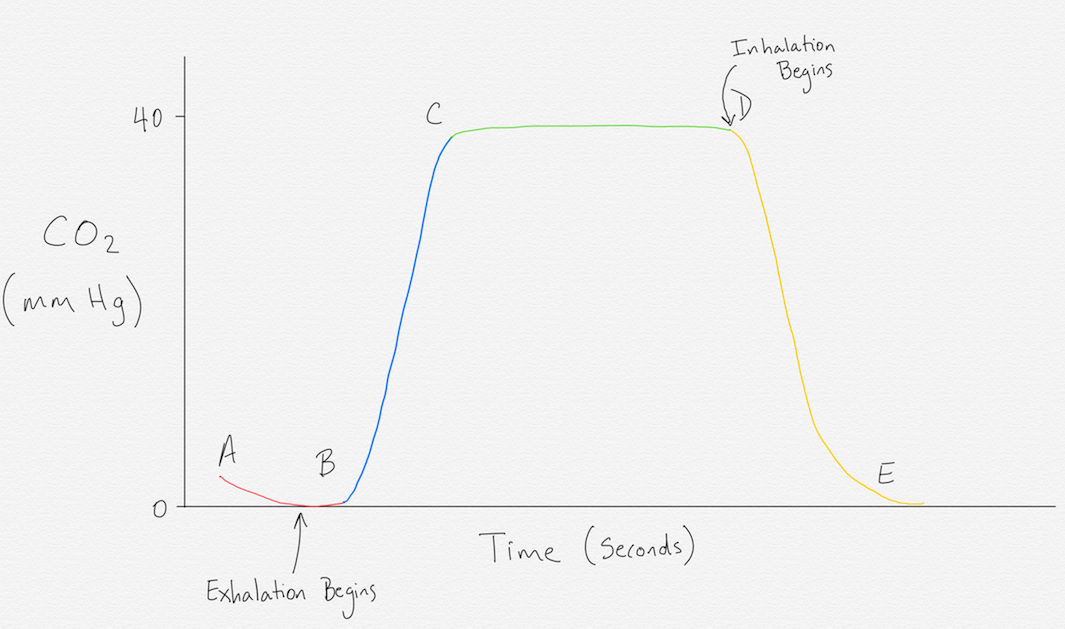
Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. End-tidal carbon dioxide and outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in. To identify whether any level of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 measured during cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR correlates with return of spontaneous circulation ROSC or survival in adults experiencing cardiac arrest in any setting. Two very practical uses of waveform capnography in CPR are.
MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST. Capnography can be used to measure end-tidal CO 2. 428 153 mmHg versus 323 141 mmHg.
In mmHg the PetCO2 values for those with and without ROSC after five minutes of CPR was. This will cause a decrease in the ETCO2 end-tidal CO2 and this will be observable on the waveform as well as with the numerical measurement. Systematic review and meta-analysis of end-tidal carbon dioxide values associated with return of spontaneous circulation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. 1 evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions and 2 identification of ROSC. Capnography waveforms etCO2 and breathing patterns.
Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition. 10 to 20 mmHg during CPR was strongly associated with ROSC while persistent EtCO2 below 10 to 20 mmHg after 20 minutes of CPR had a 05 likelihood of ROSC. Wayne MA Miller CC.
In the field monitoring ETco 2 during endotracheal-tube placement can verify correct tube placement and indicate tube dislodgement during transport. These levels of CO 2 were consistent with effective chest compression generating reasonable pulmonary blood flow justifying continuation of resuscitation. The first sign of the return of spontaneous circulation ROSC during CPR is increase in ETCO2 therefore monitoring of ETCO2 provides very useful information to guide treatment during CPR 8 - 10.
The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. 20 mmHg at 20 minutes CPR - higher chance of ROSC. Carbon Dioxide During Normal Heart-Lung Function.
N Engl J Med. End-tidal CO2 may be useful here as an easily and immediately measurable index of changes in cardiac output. J Intensive Care Med.
Abrupt increase in ETCO2 suggests ROSC during CPR detectable before pulse check. The purpose of this systematic review is to evaluate the prognostic value of ETCO2 during cardiac arrest and to explore whether ETCO2 values could be utilised as a tool to predict the outcome of resuscitation. An increase in etCO2 by 5 appears to have reasonable sensitivity 71-91 and specificity 94-100 for fluid responsiveness in two studies of patients breathing passively on the ventilator.
NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not misinterpret as ROSC. 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition.
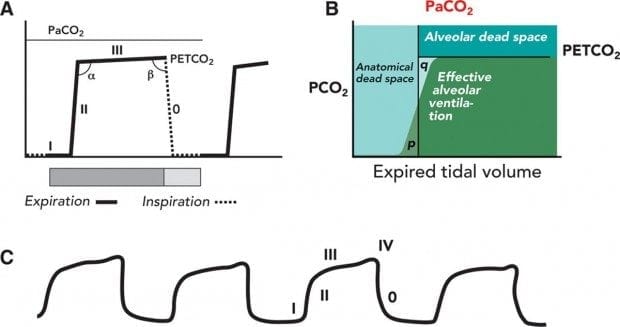
The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle. On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing. Ensure proper rate approximately 100min.
We included randomized controlled trials cohort studies and case-control studies of adult cardiac. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor.

Pdf Applications Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Monitoring In Emergency Department A Narrative Review

Part 7 Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Circulation

China Portable Ca60 Handheld Capnography Co2 Monitor Micro Mainstream Etco2 Sensor China Portable Capnography Monitor Co2 Monitor
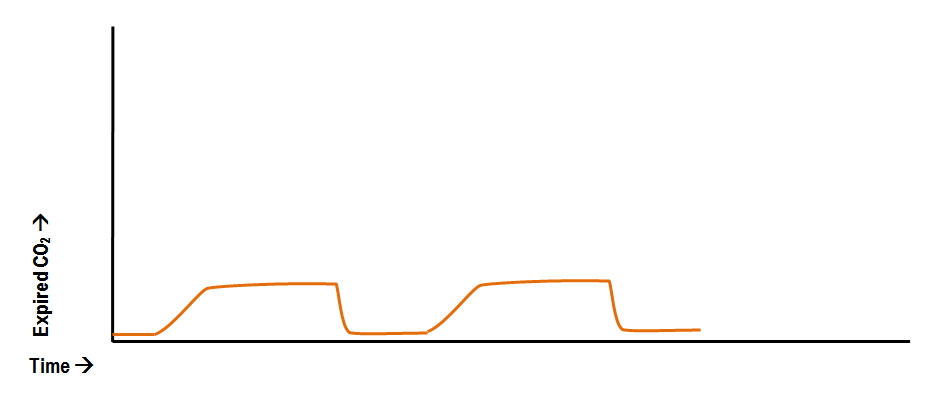
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology

Left Carotid Artery Blood Flow In The Manual Cpr And Lucas Cpr Groups Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Applications Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Monitoring In Emergency Department A Narrative Review
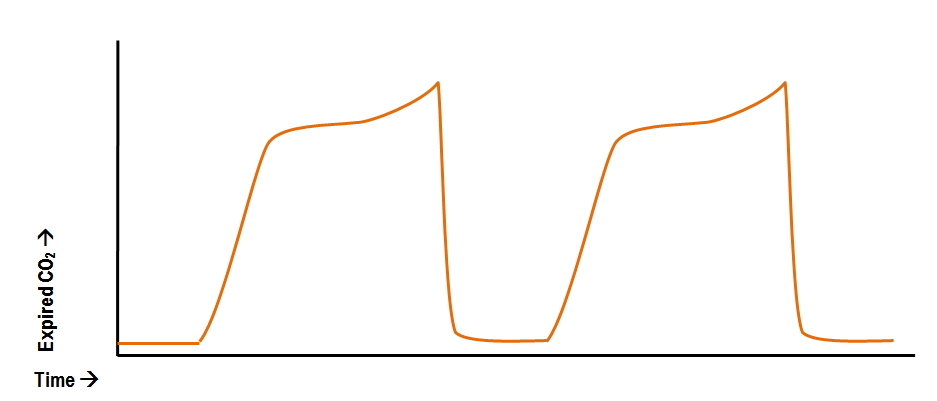
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology

Pdf Applications Of Capnography In Airway Management Outside The Operating Room Semantic Scholar

Masimo Emma Mainstream Capnograph L Portable Real Time Capnography

Resources Capnography 101 The Basics Emtprep

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Monitoring Nyu Langone Health

Advanced Cardiac Life Support Ppt Download
Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment

Critical Care Monitoring Etco2 And Hemodynamics By Louise Baartz Yazan Safi And Sunil Thomas Ppt Download